REFLEXES: A Co-Designed Architecture for In-Network Control
PIs: Sandra Hirche (TU Munich), Klaus Wehrle (RWTH Aachen University)
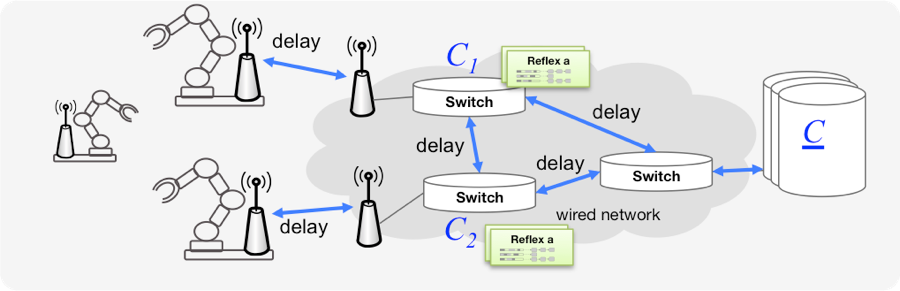
Recent technological developments in sensing, communication, control and computation have fostered an emerging class of complex applications, called Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS). In these networks, a process is no longer bound to a specific independent device, but coordinated between several interdependent network nodes; and therefore distributed via a communication network. CPS are making inroads into an ever increasing number of application domains such as industrial automation (Industry 4.0), energy, transport, and health care systems. The deployment of CPS promises considerable benefits, including increased flexibility, efficiency, and adaptability.
However, the traditional separate and layered design of communication and control architecture prevents the ubiquitous adoption of CPS as the communication-induced unreliability and latency compromises the quality-of-control and may even lead to dangerous behavior. The core concept of the project has an analogy in nature: Within the human body reflexes are fast pre-defined simple action patterns, which are located in the spinal cord, i.e. close (in the sense of low transmission latency) to the sensors and actuators. Higher-level planning and control mechanisms are located farther away in the brain.
Therefore, the goal of this project is to develop a novel co-designed architecture for communication and control to facilitate the best possible performance of CPS given the available communication and computation resources. We introduce the novel paradigm of in-network control, which pushes control functionalities as close as possible to the process to be controlled exploiting the computational power of active network components - even if limited. We will move away from the ‘traditional’ layered communication architecture and deploy in-network processing of simple control commands bypassing the classical protocol stack. In short, the general objective of this project is to reduce the communication distance of control messages as much as possible (horizontally, in the number of hops, and vertically, in the time for processing) and to increase reliability by introducing deterministic processing of such messages. As a result unnecessary time delays and unreliability within the closed control loop are avoided leading to the best possible quality-of- control. The key methodical contributions of this project are i) a novel approach to distribute the control on a given communication and computation infrastructure including appropriate analysis tools for performance evaluation, ii) a novel software framework for in-network processing with real-time constraints by co-designing the execution of control and communication procedures in a single and fundamentally new methodology.
Principal Investigators
Involved PhD candidates
Publications
- Felix Rath, Johannes Krude, Jan Rüth, Daniel Schemmel, Oliver Hohlfeld, Jó Agila Bitsch Link and Klaus Wehrle: SymPerf: Predicting Network Function Performance, ACM SIGCOMM 2017 Poster.
- Touraj Soleymani, Sandra Hirche, John S. Baras, Value of Information in Minimum-Rate LQG Control, IFAC-PapersOnLine, Volume 50, Issue 1, 2017, Pages 8963-8968, ISSN 2405-8963
- Soleymani, Touraj, Sandra Hirche, and John S. Baras. “Event-triggered output-feedback H∞ control with minimum directed information.” In 2017 IEEE 56th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), pp. 6088-6094. IEEE, 2017.
- Soleymani, Touraj, Sandra Hirche, and John S. Baras. “LQG control via wireless sensor networks with minimal transmission power.” IFAC-PapersOnLine 51, no. 7 (2018): 51-56.
- Soleymani, Touraj, Samuele Zoppi, Mikhail Vilgelm, Sandra Hirche, Wolfgang Kellerer, and John S. Baras. “Covariance-based transmission power control for estimation over wireless sensor networks.” In 2018 European control conference (ECC), pp. 857-862. IEEE, 2018.
- V. Causevic, A. Falsone, D. Ioli, M. Prandini: Energy management in a multi-building set-up via distributed stochastic optimization, Proceedings of American Control Conference (ACC), 2018.
- V. Causevic, P. Ugo Abara, S. Hirche: Information-constrained Optimal Control of Distributed Systems with Power Constraints, European Control Conference (ECC), 2018.
- Daniel Schemmel, René Glebke, Mirko Stoffers and Klaus Wehrle: Towards Benchmark Optimization by Automated Equivalence Detection, Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Benchmarking Cyber-Physical Networks and Systems (CPSBench’18), April 2018.
- Jan Rüth, René Glebke, Tanja Ulmen and Klaus Wehrle: Demo: Towards In-Network Processing for Low-Latency Industrial Control, Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2018 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, April 2018.
- Jan Rüth, René Glebke, Klaus Wehrle, Vedad Causevic and Sandra Hirche: Towards In-Network Industrial Feedback Control, Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2018 1st Workshop on In-Network Computing (NetCompute 2018), Budapest, Hungary, August 2018.
- P. Ugo Abara, V. Causevic, S. Hirche: Quadratic Invariance for Distributed Control Systems with Intermittent Observations, Proceedings of the 57th IEEE CDC 2018 - IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, December 2018.
- René Glebke, Martin Henze, Klaus Wehrle, Philipp Niemietz, Daniel Trauth, Patrick Mattfeld and Thomas Bergs: A Case for Integrated Data Processing in Large-Scale Cyber-Physical Systems, Proceedings of the 52nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Wailea, HI, USA, January 2019.
- Sebastian Gallenmüller, René Glebke, Stephan Günther, Eric Hauser, Maurice Leclaire, Stefan Reif, Jan Rüth, Andreas Schmidt, Georg Carle, Thorsten Herfet, Wolfgang Schröder-Preikschat, Klaus Wehrle: Enabling Wireless Network Support for Gain Scheduled Control, 2nd International Workshop on Edge Systems, Analytics and Networking (EdgeSys ‘19), Dresden, Germany, March 2019.
- René Glebke, Johannes Krude, Ike Kunze, Jan Rüth, Felix Senger, Klaus Wehrle: Towards Executing Computer Vision Functionality on Programmable Network Devices, 1st ACM CoNEXT Workshop on Emerging in-Network Computing Paradigms (ENCP ‘19), Orlando, FL, USA, December 2019.
- Zoppi, Samuele, Touraj Soleymani, Markus Klügel, Mikhail Vilgelm, Sandra Hirche, and Wolfgang Kellerer. “Transmission power control for remote state estimation in industrial wireless sensor networks.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.07018 (2019).
- Causevic, V., Y. Fanger, T. Brüdigam, and S. Hirche. “Information-Constrained Model Predictive Control with Application to Vehicle Platooning.” IFAC-PapersOnLine 53, no. 2 (2020): 3124-3130.
- Causevic, Vedad, and Sandra Hirche. “Distributed Optimal Control over Bit-rate Constrained Networks with Communication delay.” In 2020 59th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), pp. 724-730. IEEE, 2020.
- Causevic, Vedad, Precious Ugo Abara, and Sandra Hirche. “Optimal power‐constrained control of distributed systems with information constraints.” Asian Journal of Control 24, no. 5 (2022): 2049-2061.
- Soleymani, Touraj. “Value of Information Analysis in Feedback Control.” PhD diss., Technische Universität München, 2019.
- Jörg Christian Kirchhof, Martin Serror, René Glebke, and Klaus Wehrle: Improving MAC Protocols for Wireless Industrial Networks via Packet Prioritization and Cooperation, International Symposium on a World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks: Workshop on Communication, Computing, and Networking in Cyber Physical Systems (WoWMoM-CCNCPS’2020)
- Ike Kunze, René Glebke, Jan Scheiper, Matthias Bodenbenner, Robert H. Schmitt, and Klaus Wehrle: Investigating the Applicability of In-Network Computing to Industrial Scenarios, IEEE International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS ‘21)
- V. Causevic; P. Ugo Abara; S. Hirche: Optimal power‐constrained control of distributed systems with information constraints, Asian Journal of Control, 2021
- René Glebke, Jan Scheiper, Stefan Lenz, Mirko Stoffers, and Klaus Wehrle: Harnessing Cooperative Anycast Communication for Increased Resilience in Wireless Control, IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC 2022)